Dataverse Launches Prompt Columns: Transform Your Tables with Gen AI
Principal Program Manager at Microsoft Power CAT Team | Power Platform Content Creator
Gen AI enhances Dataverse with prompt columns for dynamic values, automating tasks in Power Platform solutions.
Key insights
- Prompt Columns in Dataverse allow users to add fields powered by generative AI that dynamically generate values using natural language prompts, making tables more interactive and intelligent.
- These columns can reference other data within the same row, enabling business-specific logic such as sentiment detection, feedback classification, action suggestions, and drafting responses directly from table data.
- Dynamic Data Analysis: Prompt Columns automate tasks like sentiment analysis and feedback categorization, providing real-time insights and reducing manual work for improved decision-making.
- The technology enables real-time integration with analytics tools, ensuring up-to-date information for workflow automation and business operations.
- This approach blends structured data (like standard database fields) with AI-generated context, allowing businesses to analyze both structured and unstructured information together for deeper insights.
- Dataverse acts as a unified platform supporting both human collaboration and AI-driven automation, helping companies scale their processes efficiently across multiple agents or teams.
Revolutionizing Data Tables with Generative AI
Microsoft’s recent introduction of Prompt Columns in Microsoft Dataverse is changing the way organizations manage and interact with their data. In a detailed YouTube video by Reza Dorrani, viewers are guided through the practical implications of this feature, showcasing how generative AI can be embedded directly into business tables. This advancement allows users to not only store information but also dynamically generate insights, automate decision-making, and enhance operational workflows with ease.
Previously, Dataverse tables were restricted to static or manually updated columns. Now, with Prompt Columns, businesses can tap into the power of natural language processing and AI-driven logic directly within their datasets. This blend of automation and intelligence aims to simplify complex tasks, streamline feedback analysis, and improve overall efficiency.
How Prompt Columns Work in Real-World Scenarios
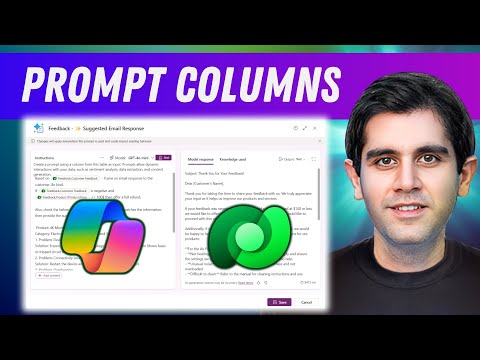
In his video, Reza Dorrani demonstrates these capabilities using a Product Feedback table. By integrating Prompt Columns, he showcases how companies can detect sentiment in review text, classify feedback types—such as bug reports, feature requests, or compliments—and even suggest next steps or responsible teams for follow-up. The ability to generate draft response emails based on feedback further highlights the practical value of this technology.
This approach leverages the underlying data within each row, allowing Prompt Columns to reference other fields and build business-specific logic. As a result, organizations can move beyond basic data storage and instead generate actionable insights and recommendations in real time, all powered by simple natural language prompts.
Tradeoffs and Challenges in AI-Driven Automation
While the benefits of Prompt Columns are clear, there are important tradeoffs to consider. Automating tasks such as sentiment analysis or feedback classification can save significant manual effort; however, relying heavily on AI-generated outputs may introduce risks if not carefully monitored. For example, AI models might misinterpret nuanced feedback or generate generic responses that require human oversight.
Balancing automation with accuracy remains a challenge. Businesses must ensure that their AI models are trained on relevant data and that there are mechanisms for validating AI-generated suggestions before acting on them. This need for oversight highlights the importance of combining human expertise with AI capabilities, rather than replacing it altogether.
Benefits and Flexibility for Business Operations
One of the standout advantages of Prompt Columns is their ability to provide real-time insights that adapt to changing business needs. By automating data analysis and response generation, companies can respond more quickly to customer feedback, market changes, or operational issues. Furthermore, the integration of AI within Dataverse supports seamless collaboration between human users and automated agents, ensuring that workflows remain efficient and consistent.
The scalability of this solution also means that organizations can extend AI-driven automation across various departments and processes. Whether it’s handling customer inquiries, processing invoices, or managing claims, Prompt Columns offer a flexible approach to embedding intelligence directly into operational data.
What Sets This Approach Apart?
The integration of generative AI into structured data tables represents a significant shift from traditional data management. By merging structured and unstructured data analysis, Microsoft Dataverse enables organizations to extract more value from their information assets. This unified approach not only improves agent operations but also supports more sophisticated multi-agent workflows, where consistent data handling and automation are critical.
Ultimately, Prompt Columns empower businesses to move from reactive data management to proactive, AI-enhanced decision-making. As Reza Dorrani’s demonstration illustrates, this technology has the potential to drive innovation, efficiency, and smarter business outcomes, all while maintaining the necessary balance between automation and human judgment.
-and-document-management-system-with-privacy-theme-concept.-businessman-publish-protected-document-connected-with-users,-access-rights-symbolized-by-key..jpeg?w=700&output=webp)
Keywords
Supercharge Tables Gen AI Prompt Columns Dataverse AI Integration Data Management Microsoft Power Platform