Microsoft Copilots: AI Agents Explained
Microsoft expert on Copilots AI agents and builders enterprise data guardrails with Power Platform Graph Entra Purview
Key insights
- Microsoft Copilots & AI Agents
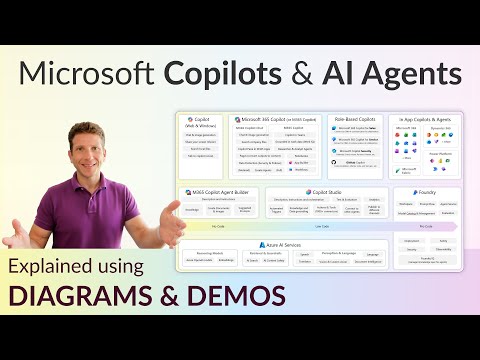
Video explains the unified AI layer that places Copilots across Microsoft 365, Dynamics 365 and the Power Platform while introducing autonomous AI agents that run multi-step workflows. - Copilot Experiences
Copilots act as a natural-language entry point inside apps like Outlook, Teams, Word, Excel and PowerPoint, offering context-aware assistance such as chat, task orchestration and organizational memory (Work IQ). - Autonomous AI Agents
Agents perform end-to-end tasks—for example, coordinating sales processes, handling expenses or maintaining SharePoint—by chaining steps, calling tools and accessing data without repeating prompts. - Builder Tools
M365 Agent Builder, Copilot Studio and Azure AI Foundry (plus AI Studio and connectors) let teams create, connect and tune agents and domain models for specific business needs. - Data & Guardrails
Enterprise deployment depends on a guardrail layer—Graph, Entra identity, Purview governance, security controls and content safety—to manage access, privacy and trust for agent actions. - Business Benefits
The ecosystem boosts productivity and automation, improves decision support, simplifies security and enables custom, scalable solutions managed like software lifecycles.
Video summary
Dani Kahil’s YouTube video presents a concise, practical diagram that maps out Microsoft’s modern AI ecosystem, focusing on Copilots and AI agents. The video explains how Copilots appear across Microsoft 365, Dynamics 365 and the Power Platform, and it shows where builders create agents using tools such as M365 Agent Builder, Copilot Studio and Foundry. Kahil also highlights a crucial layer he labels Data & Guardrails, which includes platforms like Graph, Entra and Purview that make enterprise AI deployable and trustworthy. Overall, the presentation aims to clarify roles, toolchains and protections so organizations can plan real-world AI deployments.
Where Copilots and agents integrate
According to the video, Copilots act as the primary conversational interface for everyday productivity apps, embedded in solutions such as Outlook, Teams, Word, Excel and PowerPoint. Moreover, Kahil notes that Copilots extend into vertical and role-based products within Dynamics 365, where they support sales, supply chain and other domain workflows. At the same time, autonomous AI agents orchestrate multi-step processes, moving beyond single prompts to perform tasks like coordinating receipts, updating records and executing cross-app actions. Consequently, organizations can combine a conversational entry point with agentic automation to streamline both simple and complex work.
Tools for AI builders and engineers
The video outlines a layered builder ecosystem that distinguishes between citizen creators and technical teams, and it describes tools for both audiences. For low-code and no-code scenarios, Kahil points to enhancements in the Power Platform and Copilot Studio that let business users configure behavior and connectors, while technical engineers use platforms such as Azure AI Foundry and AI Studio to assemble custom models and connectors. In addition, he emphasizes lifecycle practices similar to DevOps—covering testing, deployment and monitoring—to keep agents reliable as they evolve. Thus, the ecosystem supports a spectrum of makers, from business analysts to AI engineers, each with tailored toolchains and responsibilities.
Data, security and guardrails
Crucially, Kahil spends time on the governance layer that enables safe enterprise AI, showing how services like Graph, Entra identity, and Purview data controls form a backbone for compliant deployments. He explains that integrating these platforms provides access control, data lineage and content safety features so organizations can limit exposure and demonstrate auditability. Furthermore, Microsoft’s security-focused products, which the video groups under the broader Copilot and agent landscape, unify detection and response capabilities to manage risk at scale. As a result, enterprises can balance AI innovation with regulatory and security requirements by design.
Benefits, tradeoffs and practical decisions
Kahil’s analysis highlights several clear benefits such as improved productivity from automation, richer insights through organizational memory and faster decision-making with agent-assisted workflows. However, he also notes tradeoffs: adopting advanced agents can introduce complexity in integration, require stronger governance, and increase dependency on platform updates and vendor services. Therefore, organizations must weigh gains in efficiency against potential costs in operational overhead, integration effort and future flexibility. In practice, teams should pilot specific scenarios to measure value while iterating on guardrails and monitoring.
Operational challenges and next steps
The video does not shy away from practical challenges: debugging agent behavior, managing data consistency across apps, and maintaining trust as agents act autonomously remain difficult tasks for many teams. Kahil recommends clear owner responsibilities, continuous testing, and staged rollouts so humans stay in the loop until agents are proven reliable, and he underscores the need for ongoing training and governance rather than one-time configurations. Finally, he presents the ecosystem as a maturing platform—one that requires thoughtful strategy, cross-functional collaboration and incremental adoption to capture benefits while containing risk. Consequently, leaders should prioritize use cases that offer measurable impact and align governance with business goals before scaling broadly.

Keywords
Microsoft Copilot, Copilot for Microsoft 365, Microsoft AI ecosystem, AI agents Microsoft, Azure OpenAI Service, Copilot Studio, enterprise AI assistants, Microsoft generative AI