Excel Tips: Create Multi-Step Data Entry Forms Easily
Co-Founder at Career Principles | Microsoft MVP
Excel, PowerPoint, VBA
Key insights
-
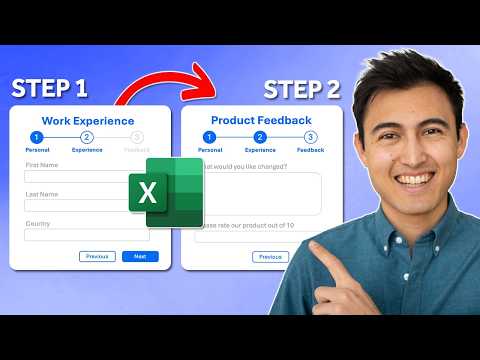
Multi-Step Data Entry Form: This form in Excel divides data input into several steps or sections, making it easier for users to enter complex information. Instead of one long form, users fill out smaller parts at a time, which helps reduce mistakes and makes the process clearer.
-
VBA UserForms: By using Visual Basic for Applications (VBA), you can create custom forms with multiple pages. Each step can have textboxes, checkboxes, and navigation buttons like "Next" and "Back." VBA also lets you validate data before moving to the next step and automatically save entries into your Excel sheet.
-
Macros and Automation: Macros help automate tasks such as transferring form data to your database or log. You can program conditional logic so that certain fields appear only when needed. Macros also make it easy to clear forms, switch between sections, and protect forms from accidental changes.
-
User Interface Design: You can design interactive dashboards or home pages in Excel with buttons that open different steps of the form. These layouts use VBA to show multi-step behavior and keep the workspace organized for better usability.
-
Templates and Examples: There are ready-made templates for tasks like employee registration or order entry that follow a multi-step flow. These templates are customizable for various business needs and save time when setting up new forms.
-
Main Benefits: Multi-step forms improve data accuracy, provide a more user-friendly interface, support automation through macros, allow customization for different uses, and enable collaboration by supporting multiple users in shared workbooks.
Introduction to Multi-Step Data Entry Forms in Excel
In a recent YouTube video, Kenji Farré, also known as Kenji Explains and recognized as an MVP, demonstrates how to create a multi-step data entry form in Excel. This technique is increasingly important for professionals who manage complex datasets or require a user-friendly way to collect structured information. By breaking down the data entry process into manageable steps, users can focus on one section at a time, which reduces errors and streamlines workflows. Kenji’s video walks viewers through each phase of building such a form, emphasizing both design and automation.
The tutorial begins by outlining the value of multi-step forms, which are especially useful when single-page forms become overwhelming or risk data inaccuracy. As organizations look for ways to improve data collection, understanding these approaches is essential for both efficiency and accuracy.
Traditional Versus Modern Approaches to Data Entry
Traditionally, Excel provides a built-in data entry form that connects directly to tables. This tool allows users to enter, edit, or navigate records one at a time, offering basic navigation with keyboard shortcuts such as Tab and Shift + Tab. However, this method is limited to single-step entry, which may not be suitable for more complex needs.
With increasing demands for flexibility, users often find the built-in form lacking in customization and automation. The standard form does not support conditional logic, dynamic fields, or advanced navigation, all of which are addressed in the modern approaches Kenji covers in his video.
Building a Multi-Step Form: Steps and Techniques
Kenji’s video outlines a comprehensive process for creating a multi-step user form in Excel. The first step involves setting up a dedicated database worksheet to store user entries. Next, he highlights the importance of user interface design, which can be prototyped in PowerPoint and then implemented within Excel for a consistent look and feel.
Moving forward, the tutorial covers how to use Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) to create a UserForm that contains multiple pages or frames. Each page acts as a step in the data entry process, and controls such as textboxes, checkboxes, and navigation buttons are added for interactivity. Kenji emphasizes the need for data validation at each step to ensure accuracy before progressing.
Finally, the automation aspect is addressed with macros. By writing simple VBA code, users can automate the movement of data from the form to the database, control the enabling of navigation buttons, and even reset the form for new entries. This makes the system both dynamic and user-friendly, reducing manual work and minimizing errors.
Tradeoffs and Challenges in Form Design
While multi-step forms offer many benefits, there are tradeoffs to consider. On one hand, breaking forms into steps can reduce cognitive overload and improve accuracy. On the other hand, designing and maintaining these forms requires a solid understanding of VBA and Excel’s structure. Users must balance the desire for a streamlined interface with the complexity of coding and testing each element.
Another challenge lies in ensuring compatibility across different versions of Excel, as some features may not function identically everywhere. Additionally, security is a concern; macro-enabled files (.xlsm) can pose risks if not handled properly. Therefore, organizations must train their teams and implement safeguards when distributing automated forms.
Advantages and Real-World Applications
Despite the challenges, the advantages of multi-step data entry forms are significant. Stepwise input supports better data validation, while navigation buttons and UI controls make the process more intuitive. Automation through macros not only speeds up data collection but also reduces manual errors, making these forms ideal for business, finance, HR, and sales applications.
Furthermore, the ability to customize forms for specific industry needs ensures broad applicability. Shared workbooks and network folders allow for collaborative data entry, which is especially useful in multi-user environments. In summary, Kenji’s tutorial provides a practical and accessible guide for anyone looking to upgrade their Excel data entry systems.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
Kenji Farré’s video on creating a multi-step data entry form in Excel offers a valuable roadmap for professionals seeking to modernize their data collection processes. By combining thoughtful design, VBA automation, and practical examples, users can address both the limitations of traditional forms and the challenges of implementing new solutions.
As organizations continue to seek efficiency and accuracy, the adoption of multi-step forms represents a forward-thinking approach. While there are tradeoffs in terms of complexity and maintenance, the benefits of improved data quality and user experience are clear. Kenji’s insights provide a strong foundation for anyone ready to embrace these advancements in Excel.

Keywords
multi-step data entry form excel excel multi-step form tutorial create data entry form excel step by step excel form with multiple steps how to make multi-page form in excel data entry automation excel advanced forms in excel