How Azure VM Hibernation works?
Principal Cloud Solutions Architect
Maximize cost-efficiency with Azure VM Hibernation: swift resumes & lowered compute charges—ideal for sporadic usage!
Key insights
Azure VM Hibernation is a cost-effective feature allowing users to suspend their Azure virtual machines when they're not needed. This process saves the VM's in-memory state onto the OS disk and deallocates the VM to avoid accruing unnecessary compute charges.
- Cost savings: Hibernating VMs can reduce Azure compute charges by pausing billing while the VM is not in use.
- Quick restarts: VMs resume faster from hibernation due to their saved in-memory state, speeding up the continuation of operations.
- Enhanced availability: Applications become more reliable as VMs can be rapidly reactivated, potentially mitigating outages.
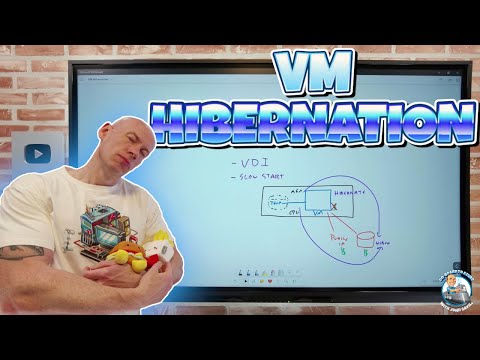
Hibernating a VM involves the operating system executing a suspend-to-disk action, storing the memory onto the OS disk, and then deallocating the VM to cease usage of compute resources.
- Efficient resumption: Memory content is swiftly transferred from the disk to memory upon restarting, minimizing downtime.
- Seamless continuity: Applications and processes resume from their prior state, providing an uninterrupted workflow.
Certain limitations apply: hibernation isn't supported for all VM types, ample disk space is needed to store memory content, and in some cases, resuming may be slower compared to starting anew.
Overall, Azure VM Hibernation serves as an advantageous tool for Azure users seeking to minimize costs while maintaining application readiness, particularly for sporadically used or reduced-demand period VMs.
Understanding Azure VM Hibernation
Azure VM Hibernation offers an ingenious way for businesses to manage their virtual resources more effectively. This feature not only optimizes operating costs by halting charges for inactive VMs but also provides agility in operations with quicker boot-up times upon reactivation. It's particularly helpful for organizations managing a fleet of VMs with fluctuating activity levels. Hibernating VMs bridge the gap between cost-efficiency and high availability, fitting seamlessly into modern cloud resource management strategies.
VM hibernation is ideal for scenarios such as development environments, where machines may remain idle overnight or for longer periods but require a quick startup. The feature allows Azure to shine in flexibility, catering to both occasional users and businesses with varying computational demands. A comprehensive understanding of the feature's benefits, workings, and limitations ensures that Azure customers can leverage VM Hibernation to its fullest potential, reinforcing the platform's position as a leading cloud service provider.
Azure VM Hibernation is an innovative feature that focuses on cost efficiency by allowing virtual machines (VMs) to hibernate when not in use. This hibernation method allows the VM's in-memory state to be saved onto its OS disk, leading to deallocation of the VM and pausing of billing for its compute resources. The introduction of this feature aims to assist Azure users in managing and reducing their compute costs effectively.
Among the key advantages of Azure VM Hibernation are reduced compute costs and faster resume times for hibernated VMs. It also helps in enhancing application availability by enabling quick rebooting in scenarios such as system outages. These benefits are crucial for optimizing the maintenance and operational aspects of VMs within Azure cloud environments.
Azure implements a specific process for hibernating VMs, which involves signaling the OS to enter a suspend-to-disk state, storing the VM's memory content on the OS disk, and eventually deallocating the VM to save costs. When resuming, the stored memory content is efficiently restored, allowing processes to pick up exactly where they left off.
Despite its advantages, Azure VM Hibernation does have limitations. Not all VM types support the hibernation feature, and sufficient disk space is required to store the VM's in-memory state. Additionally, in some cases, waking up from hibernation may be slower compared to starting the VM anew due to the need to transfer memory contents from the OS disk back to the VM's memory.
To summarize, Azure VM Hibernation offers a cost-effective solution by preserving the state of a VM, leading to significant savings and faster recovery times when compared to traditional methods. It is particularly useful for VMs that have sporadic usage patterns or those that operate predominantly during off-peak periods.
Understanding Azure VM Hibernation
Azure VM Hibernation represents a significant step in cloud computing, allowing for better cost management and flexibility in resource utilization. It serves users by offering a middle ground between fully running a VM and completely shutting it down. By understanding and effectively implementing this feature, Azure users can enhance the overall efficiency of their cloud infrastructure, ensuring that resources are used in a more economical and environmentally friendly way. With the increasing focus on cost-efficient cloud solutions, Azure VM Hibernation is set to become an indispensable tool for Azure administrators and users alike.
Understanding Azure VM Hibernation
Azure VM Hibernation is a new cost-efficient feature for managing the operational state of Azure VMs. This functionality provides significant advantages for users looking to reduce their expenditure on compute resources within Microsoft's cloud environment. The process involves preserving the in-memory state of VMs when not actively in use.
The traditional method of dealing with VMs when they're not needed is to deallocate them, which stops incurring compute costs. Azure VM Hibernation takes this a step further by not only deallocating VMs but also saving their current state, which leads to faster resume times upon reactivation. It helps in quickly bringing services back without fully rebooting the machines.
Key Points Discussed in the Video:
- The user is walked through the hibernation and resume procedures for Azure VMs.
- Benefits like cost reduction, quicker startup times, and higher application availability are outlined.
- Procedure steps and limitations of the Azure VM Hibernation feature are highlighted.
The discussion starts by differentiating the standard VM deallocation process from the new hibernation procedure, demonstrating the latter as a superior option. The feature is described as a money-saver and an enabler of faster operational resumption for VMs, which makes hibernation a strategically favorable choice.
Viewers are subsequently informed about specific requirements and limitations associated with hibernation, such as its incompatibility with certain VM types and requirements for sufficient disk space on the OS disk. There's an emphasis on understanding these constraints to effectively utilize the Azure VM Hibernation feature.
The video concludes with scenarios where utilizing Azure VM Hibernation would be most beneficial, such as with VMs running non-continuous workloads. Such use cases illustrate the practicality of hibernation in achieving both operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness within Azure environments.
Azure Master Class: More Insights
The Azure Master Class video provides a detailed walkthrough of the Azure VM Hibernation feature. It explains its application, benefits, and prerequisites, making it an invaluable resource for users looking to adopt this practice. Ensuring applications remain quickly accessible while minimizing costs is a balancing act, and Azure VM Hibernation offers a viable solution. Azure Master Class highlights how this feature is ideal for workloads with sporadic use patterns or for maintaining services with minimal disruption during outages. Mastering Azure VM Hibernation could help optimize Azure investments by reducing unnecessary compute charges while keeping VMs operationally ready at a moment's notice.

People also ask
Can you hibernate an Azure VM?
No, Azure currently does not support the hibernation of VMs. However, you can stop (deallocate) a VM to save on costs when it is not in use. Still, be aware that stopping a VM will deallocate resources and you would need to start it again for use.
How do I know when my Azure VM was shut down?
To determine when an Azure VM was shut down, you can check the activity log in your Azure portal. This log provides a detailed history of operations that were performed on the resources in your subscription, including VM start and stop times.
How do I turn off Azure VM at night?
To automatically turn off an Azure VM at night, you can use Azure Automation to create a runbook or set up a logic app that triggers the shutdown process based on a schedule you define. Alternatively, you can also use the Auto-shutdown feature available in the VM's settings in the Azure portal.
Can you pause a VM in Azure?
Azure does not have a "pause" functionality for VMs in the same way some other virtualization platforms do. The closest equivalent would be stopping the VM, which deallocates it and stops billing for compute resources while preserving the VM's state in storage, incurring storage costs.
Keywords
Azure VM Hibernation, Azure Virtual Machines, VM Sleep Mode, Azure Hibernation Feature, Cloud Computing Hibernation, Manage Azure VMs, Save Costs Azure VM, Azure VM Power Management, Azure VM Suspend, Resume Azure Virtual Machine