- All of Microsoft
Windows Power Automate: Unlock Web Automation with Structured Prompts
Structured prompts drive automation across sites with LLMS; using Azure AI, Power Automate, and Visual Studio Code
Key insights
- Structured Prompts are detailed instructions designed to help AI models understand and complete specific tasks on web pages, such as buying a product or filling out forms. These prompts make automation more accurate across different websites, even if their technical setups differ.
- Prompt Engineering Techniques like zero-shot, few-shot, chain of thought, meta prompting, and self-prompting help refine the way prompts are created. These methods ensure the AI understands tasks better and performs them efficiently.
- AI-Powered Automation combines AI models with web automation tools to handle actions like site navigation and data extraction. Using structured prompts makes these automated processes more reliable and reduces errors.
- This technology offers Improved Accuracy, Efficiency Enhancement, Increased Reliability, and Scalability. Structured prompts reduce mistakes, streamline workflows, ensure consistent results, and allow automation to work across many types of websites.
- The approach now includes a Collaborative AI and Human Approach, where AI helps generate and optimize prompts while humans guide them toward business goals. This teamwork leads to higher-quality automation outcomes.
- Adaptive and Personalized Prompts, along with Prompt Orchestration, allow AI to adjust its actions based on user needs and manage complex tasks in sequence. This makes web automation more flexible, efficient, and responsive for users.
Introduction to Structured Prompts in Web Automation
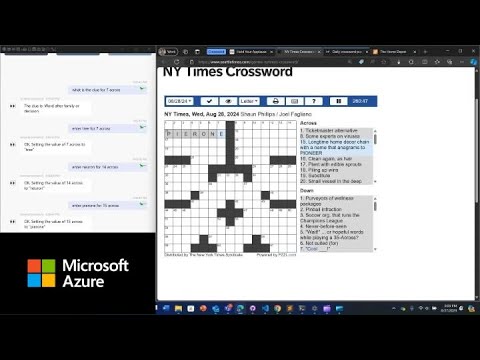
The latest Microsoft Azure YouTube video, titled "Experimental Showcase: Using Structured Prompts to Build Robust Web Automation," explores an innovative approach to automating tasks on the web. The showcase demonstrates how leveraging structured prompts with large language models (LLMs) can create logical representations of actions, such as purchasing a product, that work across various web platforms. This method stands out because it maintains a consistent logical schema, even when different sites use unique HTML and JavaScript implementations.
By focusing on structured prompts, the technology aims to deliver a more reliable and adaptable form of web automation. The video provides practical examples, including automation workflows for both crossword and e-commerce sites, emphasizing the versatility of this approach.
Understanding Structured Prompts and Their Role
Structured prompts are carefully crafted instructions that offer clear context and guidance to AI models. These prompts are essential for ensuring that the AI accurately interprets the requirements of a given task, whether it involves extracting data, filling out forms, or navigating complex web pages. In the context of this showcase, prompt engineering techniques are used to design prompts that maximize the effectiveness of AI-powered automation.
The video highlights several techniques, such as zero-shot and few-shot prompting, chain-of-thought reasoning, and meta prompting. Each technique serves to refine the interaction between humans and AI, allowing for more precise automation outcomes. This focus on clarity and context reduces ambiguity, making the automation process smoother and more dependable.
Benefits and Tradeoffs of Structured Prompt Automation
One of the primary advantages of using structured prompts is improved accuracy. By providing explicit instructions, these prompts minimize misunderstandings and reduce the risk of errors during automation. Additionally, structured prompts enhance efficiency by streamlining workflows, which in turn reduces the need for continuous manual oversight.
However, there are tradeoffs to consider. While structured prompts bring consistency and reliability, they require significant upfront effort in prompt engineering and testing. Developers must invest time to ensure prompts are comprehensive enough to handle variations across different websites. Balancing this initial investment with the long-term gains in automation quality is a key challenge.
Furthermore, the scalability offered by this approach allows organizations to automate complex tasks across multiple web applications. This scalability, though, comes with its own set of challenges, such as maintaining logical schemas that remain robust as websites evolve or change their underlying code.
Recent Innovations and Adaptive Capabilities
The showcase underscores recent advancements in prompt engineering and AI technologies. A notable development is the collaborative approach between AI and human experts. AI tools can now suggest, optimize, and generate prompts, while humans oversee the process to ensure alignment with business objectives. This collaboration not only improves the quality of the prompts but also accelerates the refinement cycle.
Another key innovation is the emergence of adaptive and personalized prompts. AI models are increasingly able to tailor their responses based on user behavior and preferences, resulting in more natural interactions and a better user experience. Additionally, prompt orchestration—organizing prompts into sequences for complex, multi-step tasks—has enabled more scalable and efficient automation workflows.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite the clear benefits, implementing structured prompts in web automation is not without its hurdles. Ensuring that logical schemas remain stable across rapidly changing web technologies demands continuous monitoring and adjustment. Moreover, as automation expands to cover a wider array of tasks, the complexity of managing and updating prompts increases.
Nonetheless, the integration of structured prompts with LLMs marks a significant leap forward in automating web-based processes. As AI models become more sophisticated and adaptive, the balance between reliability, efficiency, and flexibility will be crucial. The ongoing collaboration between AI systems and human expertise is likely to shape the future of web automation, making it more robust and accessible for businesses and developers alike.

Keywords
Experimental Showcase web automation structured prompts robust SEO techniques AI automation tools prompt engineering web scraping strategies