- All of Microsoft
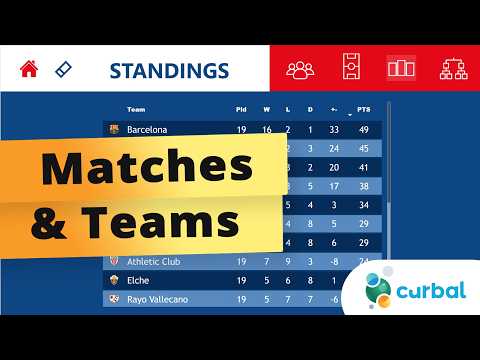
Football Project: LaLiga Matches & Teams
Microsoft Power BI La Liga expert guide adds matches and teams tables for DAX modeling, Excel integration and dashboards
Key insights
- This YouTube video shows how to add Matches and Teams tables into a Power BI model so you can analyze La Liga data in a single, organized report.
- La Liga collects huge game data — about 3.5 million data points per match from stadium cameras — and feeds it into Mediacoach for cleaning and enrichment with AI and machine learning.
- The project relies on key cloud tools such as Azure Event Hubs, Azure Data Lake, and Azure Databricks to capture, store, and process streaming match data before it reaches Power BI.
- Data modeling focuses on reliable identifiers and structure: the video explains creating unique identifiers for teams across seasons and storing hierarchical team data (home/away stats, names, logos, results) for consistent analysis.
- With properly linked tables, interactive dashboards in Power BI convert raw match stats into clear visuals, enabling tactical analysis, performance tracking, and improved reporting for clubs and broadcasters.
- The work feeds La Liga’s commercial platform, La Liga Tech, and supports stadium improvements like better stadium operations, security monitoring, and enhanced in-venue experiences.
Overview
The newsroom covered a recent tutorial video by Curbal that walks viewers through adding the Matches and Teams tables to a Power BI project focused on La Liga data. The video is part of a multi‑episode series called the Football Project and aims to show practical steps for structuring sport match data inside a business intelligence model. In addition, the presenter points viewers to downloadable pbix files and examples for hands‑on follow along, while explaining the rationale behind the table design. As a result, the tutorial serves both learners and practitioners who want a grounded example of sports analytics in Power BI.
Technical Approach
First, the author demonstrates how to ingest and shape source data before it reaches the visualization layer, emphasizing clean joins and consistent identifiers. Then, the video steps through mapping match metadata, team attributes, and match outcomes into discrete tables so that relationships remain stable across queries and seasons. Moreover, the tutorial references enterprise components often used with this architecture, such as Azure data services and processing tools that help scale ingestion and transformation in production environments. Consequently, the approach connects practical desktop techniques with concepts used in larger cloud deployments.
Next, the walkthrough highlights common transformation tasks: normalizing team names, building unique identifiers for clubs across competitions, and creating match keys that maintain integrity for home and away roles. The author explains why these steps are important for reliable analytics, because inconsistent keys or duplicate team records quickly lead to misleading results. Therefore, viewers see not only how to perform the transformations but also why they matter for downstream measures and visual logic. Finally, the video shows how to structure queries so they remain readable and maintainable for future edits.
Data Modeling: Matches and Teams
In the core demonstration, the Matches table stores match dates, venues, scores, and references to team IDs, while the Teams table holds names, logos, and hierarchical information such as club level or division. This separation reduces redundancy and improves performance when users filter by teams, competitions, or seasons, because the model can leverage relationships rather than repeated columns. Additionally, the presenter explains how to handle common issues like name changes, merged club records, and multiple competitions by building canonical identifiers and versioning when needed. As a result, the design balances normalization with practical needs for presentation.
Furthermore, the tutorial stresses data quality checks that should run before analysis, such as verifying home/away consistency and ensuring match counts align with schedule sources. Viewers learn simple tests and sample DAX measures to confirm that the data model reflects real world results, which is especially important when integrating tracking data from multiple feeds. This testing phase reduces surprises in visual dashboards and helps teams trust the numbers used for tactical or broadcasting purposes. Consequently, the model delivers credible analytics rather than isolated visualizations.
Visualization and Use Cases
After shaping the data, the video shows how to use Power BI to create interactive dashboards that highlight match events, team form, and comparative statistics across clubs and seasons. The presenter demonstrates slicers and drillthroughs that let analysts move from league‑level overviews to match‑level detail, and he discusses design choices that keep pages responsive. In particular, the tutorial points out tradeoffs between heavy visuals and performance, advising selective pre‑aggregation for common queries to maintain interactivity. Consequently, the examples are useful for clubs, broadcasters, and analysts who need fast insights without sacrificing depth.
Tradeoffs and Challenges
Balancing data granularity with system performance is the most visible tradeoff discussed, because very detailed tracking data can overwhelm desktop models and slow dashboards. Therefore, the author recommends aggregating frequent queries and using incremental refresh where possible, but he also notes that these steps add complexity and sometimes higher hosting costs. Moreover, maintaining unique team identifiers across years introduces governance overhead; it improves accuracy but requires continual maintenance or automated reconciliation workflows. Consequently, teams must weigh the benefits of cleaner analytics against the operational cost of managing those processes.
Another challenge is handling real‑time versus batch data. While near‑real‑time feeds power dynamic broadcast features, they introduce latency and cost implications compared with scheduled batch loads. The video explores both approaches and suggests hybrid architectures that use streaming for critical events and batch for historical aggregates, which balances immediacy and cost control. In practice, choosing the right strategy depends on stakeholder needs, available infrastructure, and the scale of data being processed from tracking systems.
Implications and Next Steps
Overall, the Curbal tutorial provides a clear, practical guide to building robust Matches and Teams tables for sports analytics in Power BI, and it links those desktop patterns to enterprise architectures used by major leagues. For editorial readers, the video offers a realistic view of how data modeling choices affect accuracy, performance, and cost, while also preparing teams for governance tasks that follow implementation. Finally, the tutorial leaves viewers with concrete next steps: apply the downloadable examples, test data quality, and evaluate aggregation strategies that suit local infrastructure and audience needs. As a result, organizations can make informed decisions about when to scale from a desktop proof‑of‑concept to a cloud‑driven production environment.

Keywords
La Liga Power BI, Football Power BI project, Matches and Teams tables Power BI, Power BI football dashboard, La Liga data visualization, Soccer analytics Power BI, Football data modeling Power BI, Sports analytics Power BI tutorial