
Optimize Cloud Flow History Management in Dataverse
Unlock Cloud Flow Run Insights with Dataverse Integration - Enhance Data Management Today!
Key insights
- Cloud Flow run history management is now possible in Dataverse, allowing tracking of individual Cloud Flow runs within a standard table.
- This feature enables enhanced data management and scalability by utilizing Dataverse's common data architecture and Role-Based Access control for the FlowRun data.
- Key aspects of Cloud Flows, such as start time, end time, run duration, status, and trigger type can be viewed and updated through standard Dataverse APIs or the Dataverse connector.
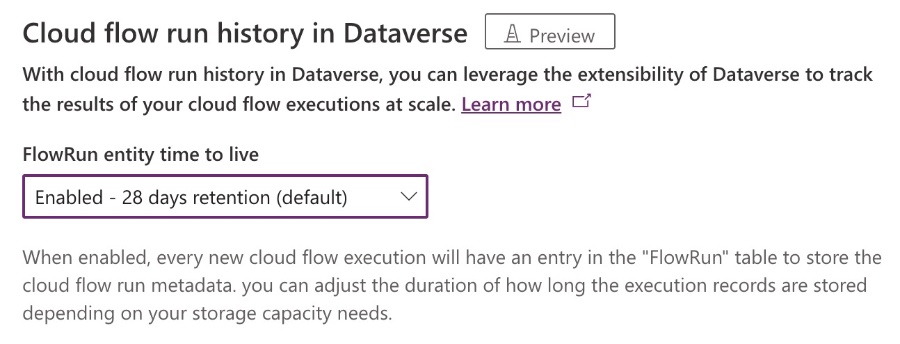
- Storage use for FlowRun records is set to 28 days by default, but users can modify this duration in the Organization table within Dataverse environments.
- The preview status of this feature indicates it may not be fully functional or available in all regions and should not be used in production environments until officially released.
- Learn more about this feature on Microsoft Site
Deep Dive into Dataverse’s Cloud Flow Run History Management
With the introduction of Cloud Flow run history management in Dataverse, businesses and developers gain unprecedented access to detailed insights into their flow executions directly within a standardized table. This capability marks a significant advancement in monitoring and managing automated processes, ensuring that users can easily track the performance, outcomes, and operational details of their cloud flows. By leveraging the extensibility and scalability of Dataverse, organizations can now apply sophisticated access control and data management strategies to their Cloud Flow run histories.
The FlowRun table, a central feature of this new functionality, provides detailed records of each flow’s execution, including crucial metrics such as start and end times, run duration, and success or failure status. This granularity allows for more precise troubleshooting and optimization of automated processes. The management of these records through standard Dataverse tools enhances user experience and integrates seamlessly with existing workflows.
Overview of Cloud Flow Run History in Dataverse
Cloud Flow run history in Dataverse marks a significant advancement, providing users the ability to save details of individual Cloud Flow runs directly into a Dataverse table. Jakub Homola's article elaborates on setting up this feature. It is crucial to note that only Cloud Flows incorporated into solutions will have their runs saved.
Key Features and Limitations
Dataverse's integration with Cloud Flow run history encourages scalable tracking of cloud flow executions. Utilizing Dataverse's architecture, including Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), enables efficient management of FlowRun data. However, it's important to remember this is a preview feature and may not be fully available or suitable for production environments.
The FlowRun table in Dataverse holds essential information about each Cloud Flow run, including start and end times, run duration, status, and error messages. This feature leverages Dataverse elastic tables for optimal performance. Nevertheless, there are limitations, such as the restriction to 20 GB per partition and the possibility of throttling for users with extensive Cloud Flow operations.
Data Storage and Management
By default, Cloud Flow run data is stored for 28 days, with options to adjust the duration. Storage consumption can be monitored and managed through the Power Platform admin center. However, FlowRun records are tied to specific owners, and currently, the concept of shared FlowRun records for collaborative flows is not supported.
Various factors may lead to incomplete FlowRun data, such as high ingestion rates or reaching storage capacity limits. Users have the option to mitigate the storage used by adjusting the Time to Live (TTL) settings for FlowRun records, thereby controlling the lifespan of the data stored.
Conclusion
This feature presents a promising development for Power Automate users looking to enhance their data management capabilities within Dataverse. Although faced with certain limitations and currently in preview, Cloud Flow run history in Dataverse offers a solid framework for tracking and managing Cloud Flow executions. Users are encouraged to explore this feature, keeping in mind the storage and management considerations outlined by Jakub Homola.

People also ask
How to see flow run history?
To view the history of your flow executions, first, ensure you're logged into Power Automate and have selected the appropriate environment. Navigate to the 'Run history' section of your flow to see past runs within the last 28 days. Note that you can download data for up to the first 100 runs based on the filter you apply, which includes options for filtering by all runs, only successful runs, or failed runs, among others.
Do Power Automate flows have version history?
In the process of developing a solution cloud flow, it is possible to save drafts to Microsoft Dataverse before finalizing the flow. Once the flow's development has reached completion, it can be published for execution. Throughout this development process, Dataverse records each saved version, creating a comprehensive version history that can be viewed in the version history panel.
How do I export Power Automate flow history?
To export the history of your flow executions, simply use the 'Export run history' feature.
Where are cloud flows stored?
Cloud-based flows are securely housed within Microsoft Dataverse, specifically in the process (workflow) table. This storage approach is consistent with that of business rules and business process flows. Although the Power Automate Management connector offers some insight into flows, certain specifics, including trigger details, are not accessible through this connector.
Keywords
Dataverse cloud flow management, cloud flow run history, manage Dataverse flow history, Dataverse flow run tracking, cloud flow history Dataverse, optimize Dataverse cloud flow, Dataverse cloud flow analytics, cloud flow performance Dataverse